
Actions address the root cause and preventive opportunities.Verify the RCA work performed is aligned to the level of Risk the problem has been identified with.Verify that appropriate Statistical Process Control (SPC) methods are used to detect recurring quality problems.Data sources for Corrective and Preventive Action are of appropriate quality and content.Tracking of Trends (which are unfavorable) are identified.Evidence that appropriate sources of product and quality problems have been identified.Verification of a CAPA system procedure(s) that addresses the requirements of the quality system regulation.The 10 objectives of CAPA implementation are:
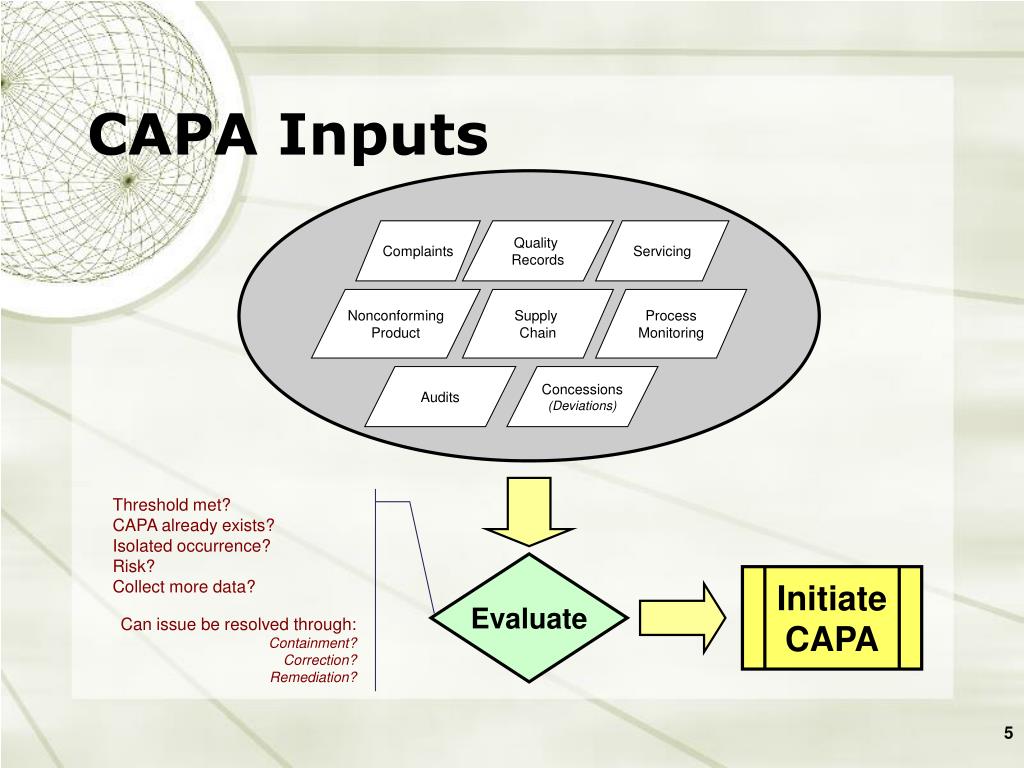
Once implemented, the CAPA system must exhibit ten objectives to meet the intent of the FDA 21 CFR 820.100 requirement. Failure to implement an effective Corrective Action Preventive Action process is a violation of FDA regulations defining Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). Symptoms can be treated but finding out why the symptom is experienced is the true purpose for implementing CAPA. When a problem occurs, it is often just a symptom of the real issue. Identifying the root cause of failure is a key tenet of any effective QMS. It is important for employees at all levels, from top management to the floor personnel, to understand the process of CAPA and its importance for an effective system.Why Implement Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA) An efficient and compliant CAPA system needs a set of data in order to identify the problems, implement solutions, and document the outcome and further changes. Corrective action is used to address systemic non-conformities when they occur while preventive actions address the risk of non-conformities that are likely to happen. CAPA has two different components, corrective action and preventive action. The 5 Whys-technique is also useful in detecting the cause-and-effect relationships inducing a particular problem.Ĭorrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) process helps an organization to analyze and collect relevant product-related information, investigate and identify product and quality problems, and trigger appropriate and effective corrective or preventive actions to eliminate a problem and prevent its recurrence. APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) is generally used in the automotive industry to drive quality improvement in mobility end products. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is another effective element of a proactive approach, that provides input for your CAPA activities. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is an analytical method that helps identify and rectify the sources of potential problems. You can use numerous techniques to improve your Corrective Action, Preventive Action approach. In case of systemic issues, Corrective Action is needed to eliminate a problem and prevent its recurrence while for non systemic issues, Preventive Action is required to reduce the risks of this adverse event occurring. Non-conformities may be determined during an internal or external audit, through customer complaints, or if reported internally.
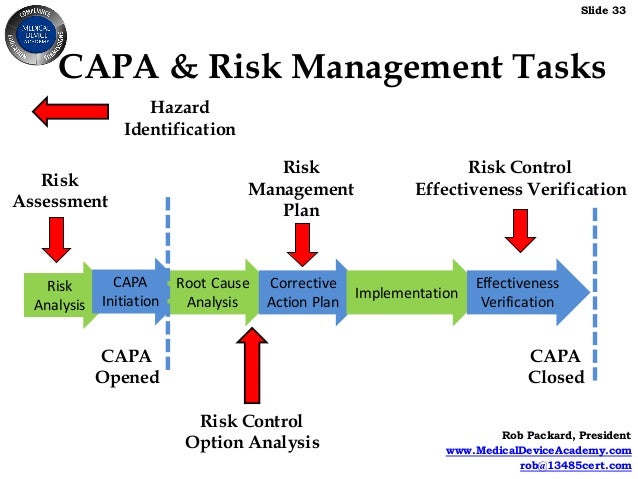
The first process will be the identification phase where you will identify non-conformities in your processes and determine what kind of problem you are looking at. Dealing with customer complaints and non-conformances is the backbone for rectifying problems but organizations can now reinforce the process throughout the digitally connected enterprise by managing CAPAs in real-time and ensuring stakeholders take impactful, proper actions.Ī general Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) process follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle to resolve unexpected events.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
